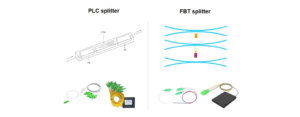
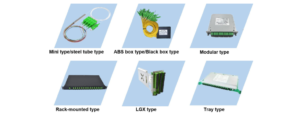
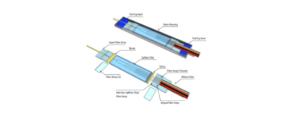
The Fiber Optical Splitter is an essential component used in an FTTH GPON where a single optical input is split into multiple outputs. This enables the deployment of a Point to Multi-Point (P2MP) physical fiber network with a single OLT port serving multiple ONTs. The most common split ratios are 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, 1:32, and 1:64. Other split ratios are available, but they are usually custom-made and command a premium. Such as 1:6, 1:12, 1:24.

Optical fiber systems are replacing coax networks, which were used to transmit CATV analog RF signals. Wavelength Division Multiplexer (WDM) Couplers are used to overlay the 1550 nm analog signal from the CATV digital transmitter at the head end to the 1310 nm and 1490 nm signal from the PON equipment.

The most common splitters deployed in a GPON system are uniform power splitters with a 1xN or 2xN splitting ratio, where N is the number of output ports. The optical input power is distributed uniformly across all output ports. Splitters with non-uniform power distribution are also available, but these are usually custom-made to user specifications.

The optical splitter in a GPON system functions to share the cost and bandwidth of the OLT among multiple ONTs, as well as reduce the number of fiber lines required in the OSP. Splitters are deployed in a centralized splitting configuration or a cascaded splitting configuration depending on the customer distribution. 1xN splitters are usually deployed in networks with a star configuration, while 2xN splitters are usually deployed in networks with a ring configuration to provide physical network redundancy.